CNC machines in the automotive industry
Efficient production processes with CNC machines
CNC machines are used in the automotive industry to manufacture a wide variety of parts. From cylinder heads to transmission and engine parts and switches, the production of a wide range of components is easily possible.
CNC machines such as CNC lathes and CNC milling machines are particularly suitable for components that have to be produced repeatedly.
CNC machines such as CNC lathes and CNC milling machines are particularly suitable for components that have to be produced repeatedly.
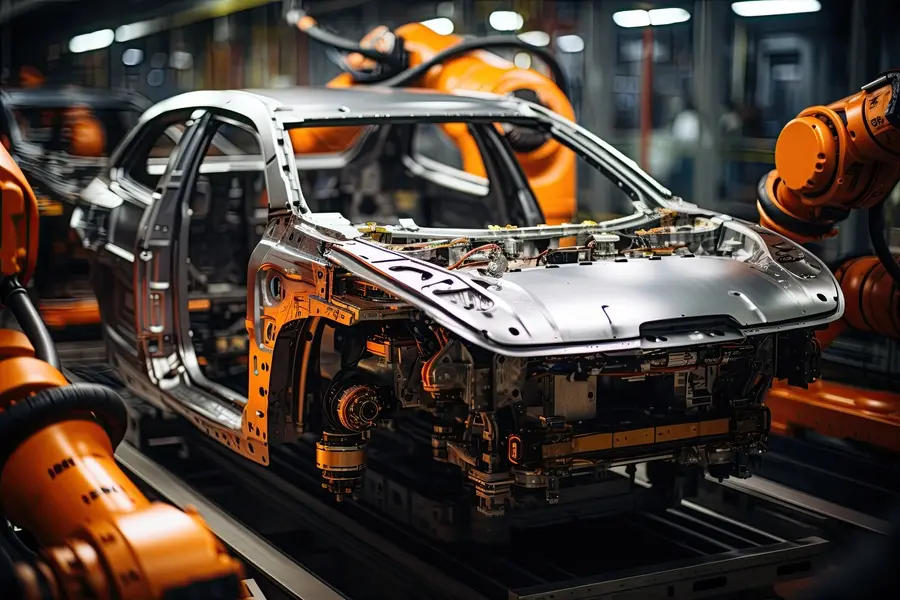

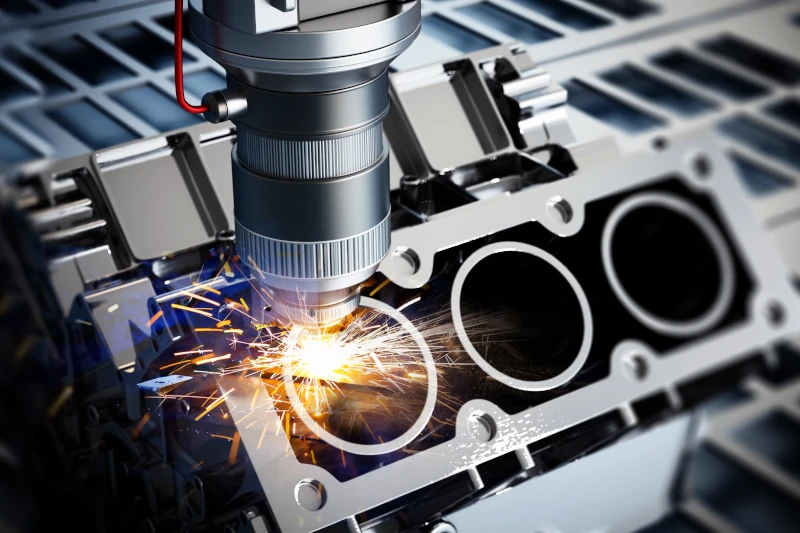
Precise processing and shaping
CNC machines are capable of producing the finest components with precision: Whether large or small, series production or special individual parts, there are no limits to the possibilities.
Even complex components can be precisely created and processed using computer-controlled CNC technology.
Even complex components can be precisely created and processed using computer-controlled CNC technology.
Benefit from cost and time optimization
Saving costs and time by using efficient CNC machines in the automotive industry is a pioneering technology. Prototypes and creative designs can be implemented quickly thanks to computer-aided technology.
Benefit from optimized manufacturing processes with CNC lathes in the automotive industry.
Benefit from optimized manufacturing processes with CNC lathes in the automotive industry.
Advantages of using a CNC machine in the automotive industry
The production of workpieces for automotive applications with CNC machines has many advantages:
- Flexibility due to the possibility of producing individual pieces as well as series production
- Cost savings through repeatability of the production pieces
- Efficiency, time savings and precision thanks to computer-aided, automated production
FAQ
How-to-Guide:
Step 1: Selecting the CNC machine
Decide which type of CNC machine is required based on the component to be produced and the required quantities. Also take into account the material requirements, the size of the parts and the complexity of the machining.
Decide which type of CNC machine is required based on the component to be produced and the required quantities. Also take into account the material requirements, the size of the parts and the complexity of the machining.
Step 2: Design and programming
Create a detailed CAD design of the desired car part. Then program the CNC machine with the CAD model to define the exact manufacturing process.
Create a detailed CAD design of the desired car part. Then program the CNC machine with the CAD model to define the exact manufacturing process.
Step 3: Setting up the CNC machine
Set up the CNC machine according to the specifications of the component. This includes inserting the correct tool, positioning the raw material and setting the necessary machine parameters.
Set up the CNC machine according to the specifications of the component. This includes inserting the correct tool, positioning the raw material and setting the necessary machine parameters.
Step 4: Test run and adjustments
Carry out a test run to ensure that the machine is programmed correctly. If necessary, make adjustments to ensure the precision and quality of the component.
Carry out a test run to ensure that the machine is programmed correctly. If necessary, make adjustments to ensure the precision and quality of the component.
Step 5: Mass production
After a successful test phase, start mass production. Monitor the production process regularly to ensure consistent quality.
After a successful test phase, start mass production. Monitor the production process regularly to ensure consistent quality.
Step 6: Quality control and post-processing
Check each manufactured part for compliance with quality standards. If necessary, carry out reworking to meet the required specifications.
Check each manufactured part for compliance with quality standards. If necessary, carry out reworking to meet the required specifications.
Step 7: Documentation and analysis
Document the entire production process and analyze the data to identify opportunities to increase efficiency and reduce costs.
Document the entire production process and analyze the data to identify opportunities to increase efficiency and reduce costs.



